Top 10 International Transportation Options for Global Shipping in 2023
In the ever-evolving realm of global commerce, the significance of effective International Transportation cannot be overstated. As businesses seek to expand their reach across borders, understanding the various options available for shipping goods internationally becomes crucial. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in International Transportation logistics, "In today's interconnected world, choosing the right transportation method can be the difference between success and setback for global businesses."
With the increasing complexity of supply chains and the demand for faster delivery times, companies must navigate a myriad of transportation options to meet the diverse needs of their customers. From air freight to maritime shipping, each avenue presents unique advantages and challenges that can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. As we delve into the Top 10 International Transportation Options for Global Shipping in 2023, it is essential to examine how these methods can enhance logistics strategies and drive sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
In light of the continuous evolution of international logistics, businesses must remain informed about the latest developments and innovations in International Transportation. This exploration not only highlights the best practices of 2023 but also sets the stage for future advancements that will shape the way goods are moved across the globe.

Overview of International Transportation Methods for Global Shipping
When it comes to global shipping, businesses are presented with a variety of international transportation methods, each tailored to different needs and circumstances. Air freight remains one of the fastest options, ideal for time-sensitive shipments, particularly for high-value or perishable goods. Though more expensive than other modes, its speed and reliability make it a preferred choice for urgent deliveries. Conversely, sea freight is often utilized for bulk shipments over long distances. While it may take longer, the cost-effectiveness and capacity of container ships can accommodate larger volumes, making it suitable for a wide range of products.
Rail transport serves as another critical international shipping method, particularly in regions with well-established rail networks. It provides a balance between time and cost, offering fast transit times compared to sea freight while still being cheaper than air transport. Additionally, road freight complements these options by providing the last-mile delivery service needed to reach final destinations. Companies often use a combination of these international shipping methods to optimize logistics and reduce overall costs, ensuring that products are delivered efficiently and effectively across borders.
Top 10 International Transportation Options for Global Shipping in 2023
Sea Freight: Advantages and Disadvantages for Global Logistics
Sea freight has long been a cornerstone of global logistics, offering distinct advantages while also presenting some challenges. One of the primary benefits of sea freight is its cost-effectiveness, particularly for bulk shipping. It's generally cheaper than air freight, making it a favorable option for companies shipping large quantities of goods across long distances. Additionally, sea freight allows for the transport of heavy and oversized cargo that might not be feasible by air. The environmental impact is also a consideration; shipping by sea tends to produce lower carbon emissions per ton-mile than other forms of transportation.
However, there are noteworthy disadvantages to sea freight that logistics operators must navigate. Transit times are significantly longer than air freight, which can be a critical factor for businesses relying on just-in-time inventory systems. Furthermore, sea freight is subject to unpredictable delays caused by adverse weather conditions or port congestion. The risk of damage or loss during transit, though mitigated by insurance, remains a concern for valuable cargo.
**Tips for Optimizing Sea Freight**:
To maximize the efficiency of your sea freight logistics, consider planning shipments well ahead of deadlines, allowing for potential delays. Additionally, working with a reputable freight forwarder can help navigate complexities in documentation and customs clearance, ensuring a smoother shipping process. Finally, regularly reviewing shipping routes and selecting ports with efficient handling operations can significantly enhance overall shipping times.
| Transportation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Cost Efficiency | Average Transit Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Freight | Lower costs for bulk goods, Environmental friendly | Long transit times, Weather dependent | High efficiency for heavy cargo | 2-6 weeks |
| Air Freight | Fast delivery, Global reach | Expensive, Limited cargo size | High cost per kg | 1-3 days |
| Rail Freight | Cost effective for long distances, Reliable | Limited routes, Not suitable for remote areas | Moderate cost | 1 week |
| Truck Freight | Door-to-door service, Flexible routes | Traffic delays, High fuel costs | Competitive for short hauls | 1-5 days |
| Intermodal Freight | Best of all modes, Increased efficiency | Complex logistics, Potential delays | Cost varies based on routes | Varied |
| Barge Freight | Cost-effective on rivers and lakes, Eco-friendly | Slow, Limited to waterways | Very low cost | Weeks to months |
| Courier Services | Fast and efficient for small parcels | Costly for heavier shipments, Limited tracking | High per parcel cost | Same day to 2 days |
| Freight Forwarding | Expertise in logistics, Cost savings | Additional handling fees, Dependence on partners | Varied, usually cost-saving | Varied |
| Drop Shipping | No inventory management, Easy to scale | Lower profit margins, Dependence on suppliers | Variable, usually profitable | Depends on supplier |
| Consolidated Shipping | Cost savings for small shipments, Reduces carbon footprint | Longer delivery times, Limited flexibility | Cost-efficient | 1-3 weeks |
Air Cargo: Speed and Efficiency in International Shipping
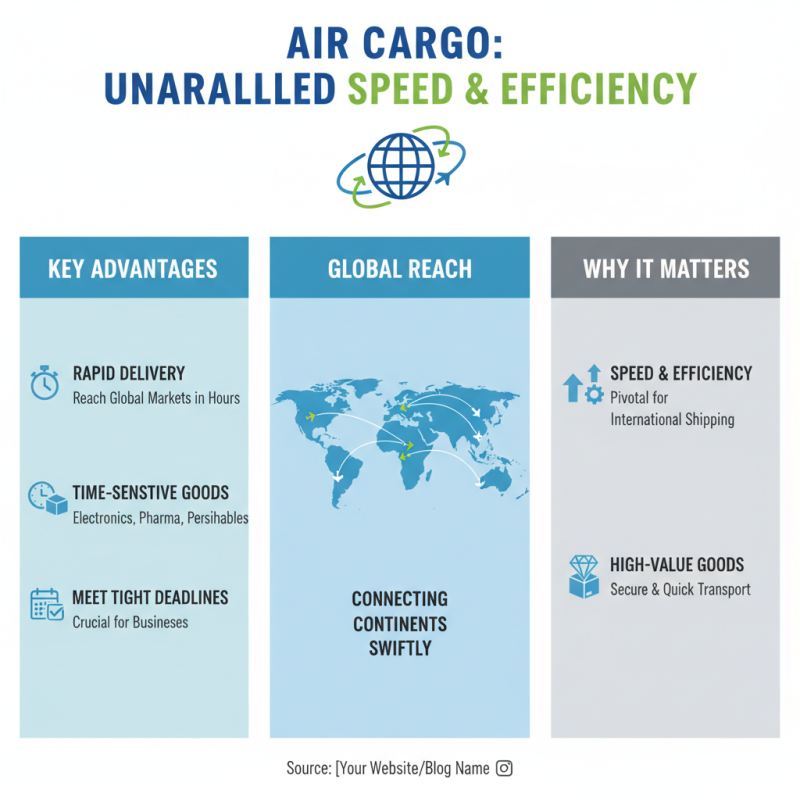
Air cargo has emerged as a pivotal component of international shipping, delivering unparalleled speed and efficiency. With the ever-increasing demand for quick delivery times, air freight offers a viable solution for businesses seeking to meet tight deadlines. This mode of transportation is particularly advantageous for time-sensitive goods such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and perishable items, allowing exporters to reach global markets in just a matter of hours.
Moreover, the efficiency of air cargo extends beyond speed. It minimizes the risks associated with delays often experienced in other transportation methods, such as sea freight. Enhanced tracking technology provides real-time updates, enabling shippers and recipients to monitor shipments closely. This transparency is crucial for managing supply chains effectively and ensuring that goods arrive safely and on time. As global commerce continues to expand, air cargo remains a reliable and essential option for companies looking to optimize their international shipping strategies.
Rail Transport: Cost-Effective Solutions for Land-Based Shipping
In 2023, rail transport continues to emerge as a pivotal component in the landscape of international shipping, offering a cost-effective solution for land-based logistics. According to a report by the International Rail Transport Union, rail freight is not only less expensive than trucking but also significantly reduces carbon emissions, making it an increasingly appealing choice for environmentally conscious shippers. Studies indicate that rail transport can lower costs by up to 40% compared to truck transportation, particularly for long-distance shipments, making it a viable option for companies looking to enhance their supply chain efficiency while controlling expenses.
Moreover, rail networks have been expanding globally, allowing for improved connectivity between key trade regions. The Rail Freight Forward initiative reports that rail freight transport accounts for approximately 18% of the total freight traffic in Europe's logistics sector. This trend is spurred by investments in infrastructure and technology, enabling faster and more reliable services. With the increasing demand for sustainable transport solutions and the necessity for efficient supply chains, rail transport stands out as a strategic choice for businesses aiming to navigate the complexities of global shipping in an economically and environmentally responsible manner.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Global Shipping Methods in 2023
In 2023, the landscape of global shipping is being reshaped by emerging technologies that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. According to a report by the International Maritime Organization, the integration of digital technologies has the potential to increase shipping efficiencies by up to 30%. Automation, particularly in logistics and port operations, is a prominent trend. Autonomous ships and drones are making headlines, with estimates suggesting that by 2030, nearly 10% of maritime cargo could be transported using these technologies. This shift not only promises to expedite delivery times but also to reduce human error in operations.
Moreover, blockchain technology is revolutionizing the tracking and transparency of shipments across international waters. Research from McKinsey & Company indicates that implementing blockchain across the supply chain could save the industry as much as $50 billion annually by improving accuracy and reducing fraud. Smart contracts enable real-time transactions and documentation, fostering a more fluid exchange between partners and stakeholders. Coupled with the Internet of Things (IoT), which allows for real-time monitoring of cargo conditions, these technologies are setting a new standard for reliability and security in global shipping practices. As these innovations continue to proliferate, businesses are urged to adapt quickly in order to stay competitive in an increasingly complex market.


